1、前言
struts是标准的"模型2"的web应用框架,其中的actionservlet代表了"模型2"mvc设计模式中的"控制器" .struts应用程序一般使用jsp代码生成用户界面,这些代码不包括任何商业逻辑,代表了mvc中的“view”部分。需要执行商业逻辑的用户界面中的表单或超链将会由"控制器" actionservlet接收和处理。在struts中,只有一个actionservlet实例,这个实例将接收和处理应用中的相关用户交互请求。actionservlet实例将选择和调用相应的action类来处理商业逻辑。在设计模式上,action类被称为“控制辅助者”,它将修改javabeans,这些javabeans就是mvc中的“ model”部分。本文将分析在struts中进行模块化编程的具体细节。
2、样例描述
我们将作一个模块编程的例子,这个例子包括三个模块,缺省模块、registration模块和approval模块。缺省模块下有资源index.html,我们使用它来连接其它两个模块。registration模块和approval模块的编程类似,都包含一个index.jsp和一个结果jsp:result.jsp.下面是目录结构:
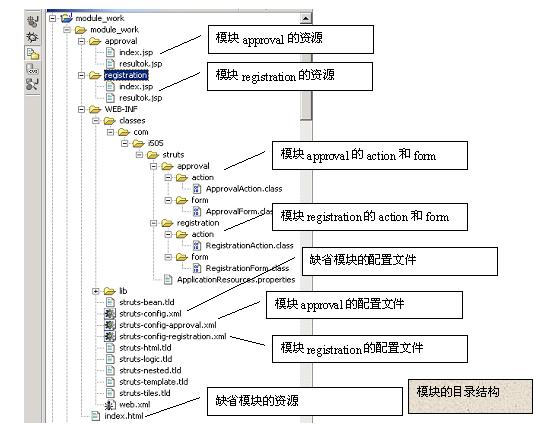
目录结构表明,struts的模块由配置文件、java类(这里者action和form类)和资源文件构成,另外各模块可以共享web.xml,message (这里是applicatonresources.properties)文件。
我们的例子的界面交互图可以表示如下:
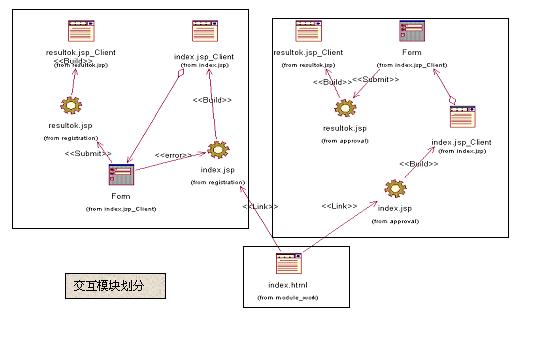
缺省模块的index.html包括两个链接,分别连接两个模块的index.jsp资源,registration模块的index.jsp提交后,如果验证失败会重新返回到该模块的index.jsp,否则用资源resultok.jsp显示注册成功的结果。模块approval的index.jsp提交后进入到resultok.jsp的界面,显示批准与否的结果。
我们从应用程序的文件组成和交互两方面的模块情况对我们要实现的例子进行了比较清晰的组织,下面我们讲解如何在struts中实现模块化编程。
3、struts的模块化机制
我们将讲解struts的相关配置,这些配置大部分与模块化编程有关系,有些没关系但对理解struts程序有利。
3.1 actionservlet参数
actionservlet有好多参数可供设置,struts在web应用部署描述符中定义这些参数:
?config――逗号相隔的应用上下文相对的配置文件的路径,这些配置文件包含了struts web应用的缺省模块的设置。缺省值为 /web-inf/struts-config.xml;
?config/${module} -逗号相隔的应用上下文相对的配置文件的路径,这些配置文件包含了struts web应用的${module}模块的设置。这个模块的前缀是/${module},多个config/${module}参数定义了多个struts web应用模块;
?convertnull - 如果这个参数的值为 true, 数值型java 包装类(比如java.lang.integer)的初始值将会是null,而不是0.缺省值[false]
?rulesets-逗号相隔的附加的org.apache.commons.digester.ruleset列表,digester在分析配置文件时,除了针对标准的配置元素的ruleset之外,还会利用这些对象来分析配置文件,这样提供了一个配置扩展机制……
?validatin - 指示我们是否使用验证型的xml分析器来处理配置文件,缺省值为 [true]
3.2 配置文件
我们说struts针对每个模块可以有一个或多个配置文件,这些配置文件使用xml来书写,下面是标准的配置文件xml的元素解释。
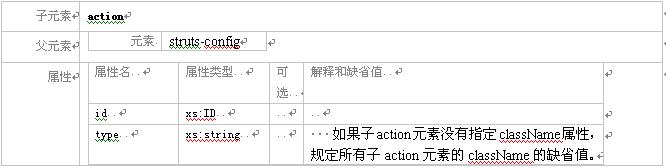
3.2.1 元素 action
这个元素描述了一个actionmapping 对象,这个对象将用来处理用户针对某个模块相对应的uri 的请求。
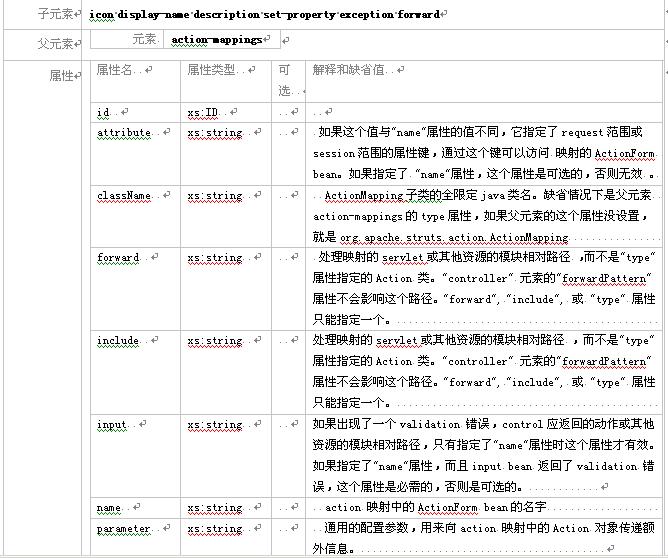
3.2.2元素 action-mappings
这个元素描述了一个actionmapping 对象集,类型是org.apache.struts.action.actionmapping.与struts的actionservlet 注册的url模式匹配的用户请求将具体地被这些actionmapping 对象处理。子元素定义了各个actionmapping对象。
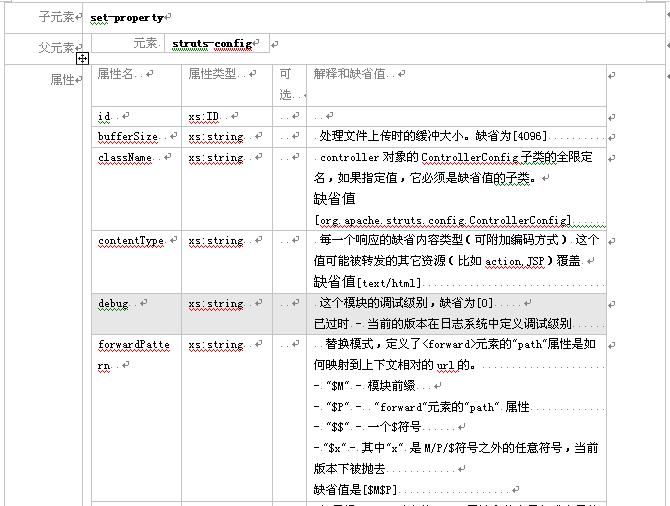
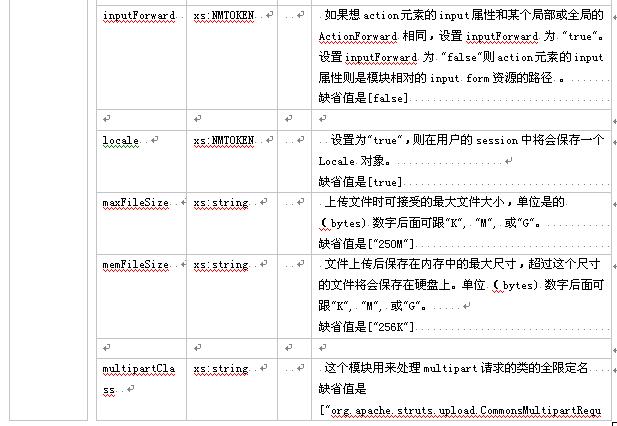
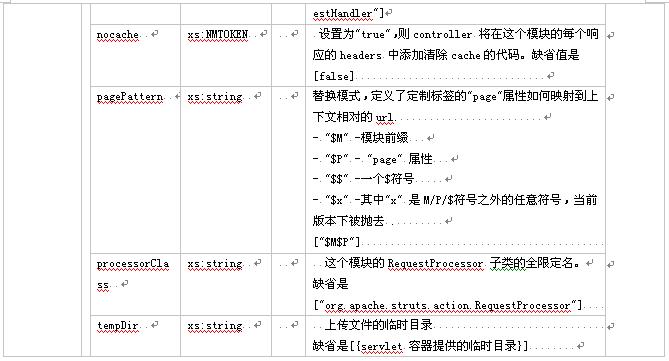
3.2.3元素 controller
这个元素描述了一个struts模块运行环境的配置――controllerconfig bean
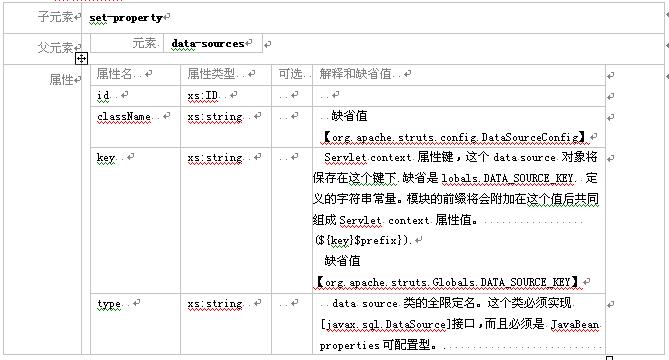
3.2.4 元素 data-source
这个元素描述了一个datasource 对象――jdbc 2.0 标准扩展。这个对象将被保存在应用上下文中,而且可以象javabean 一样被设置。
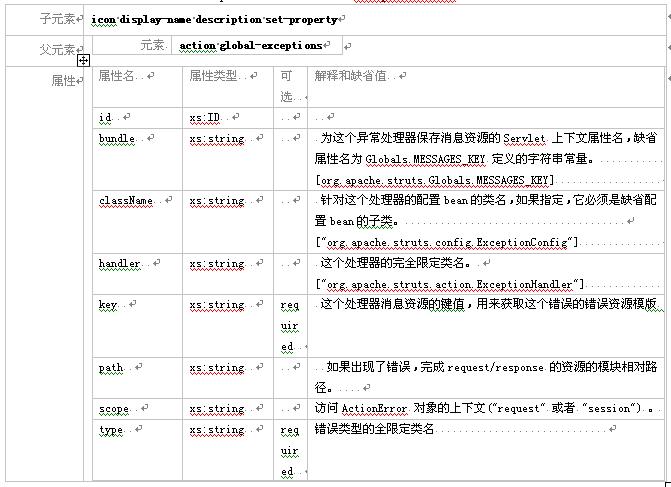
3.2.5 元素 exception
这个元素向struts系统为一个exception类型注册了一个exceptionhandler.。
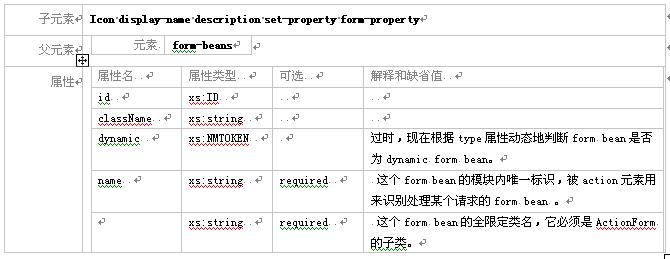
3.2.6 元素 form-bean
这个元素定义了一个actionform[org.apache.struts.action.actionform子类,这个定义被"action"元素所引用。
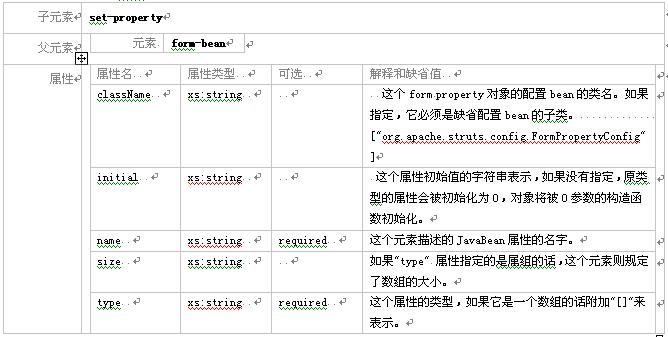
3.2.7 元素 form-property
这个元素描述了一个配置dynaactionform 或其子类的javabean属性。当这个元素的父元素"form-bean" 的"type" 是 [org.apache.struts.action.dynaactionform] 或其子类时有效。如果使用了一个定制的dynaactionform 子类,父元素"form-bean" 的"dynamic"属性必须设为 "true".
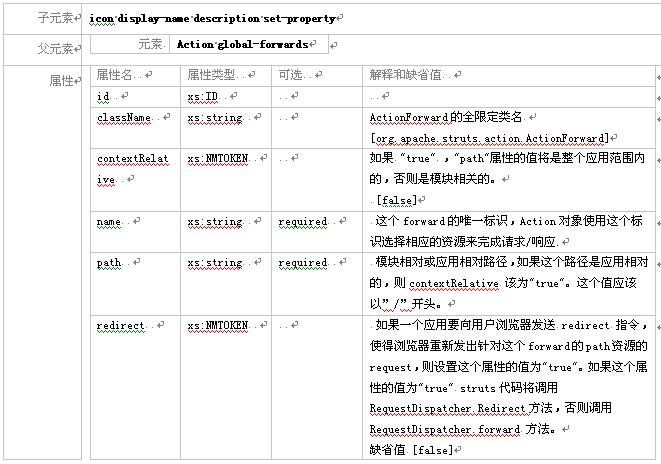
3.2.8 元素 forward
这个元素描述了一个actionforward 对象,这个对象将被action的doperform返回。在代码中一般用一个逻辑名字来引用actionforward 对象。一个"forward" 可以用来描述全局或局部actionforwards. 全局的 forwards对模块内所有的action 对象有效,局部forwards 嵌套在 元素内,只能被相应的actionmapping 中的action访问。
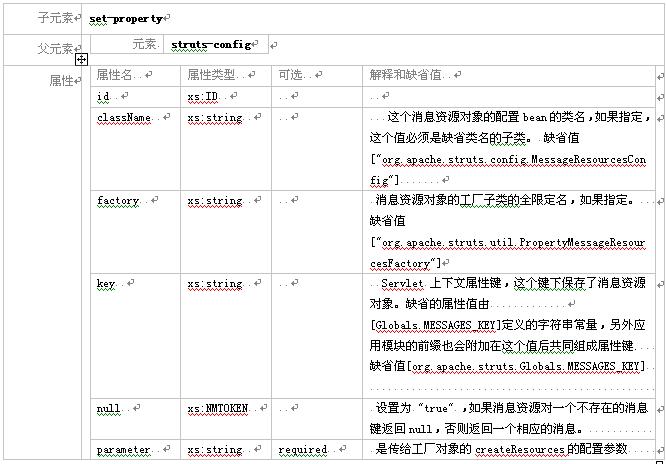
3.2.9元素 message-resources
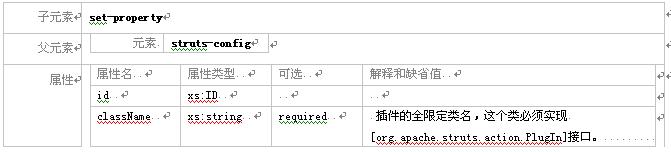
3.2.10元素 plug-in
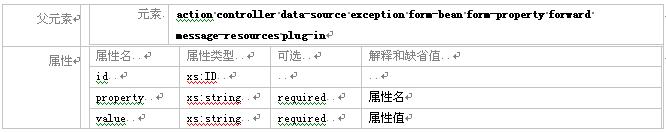
3.2.11 元素 set-property
4、模块定义
通过上面对struts的模块化机制的讲解,我们现在可以开始实现我们的模块化例子程序了。
4.1 actionservlet参数
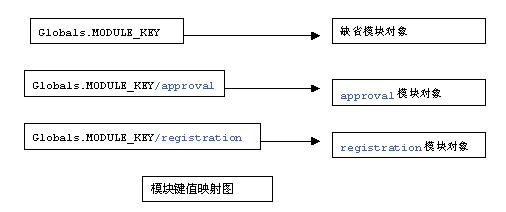
我们在struts的web.xml中定义模块。下面的代码定义了三个模块:缺省模块,approval和registration模块,前缀分别是“”,/approval和/registration.
|
这样在初始化actionservlet的过程中,servletcontext的属性中就会有这样的属性键/值关系:
4.2 approval模块配置文件
下面是approval模块的配置文件,定义了form和action,以及相应的forward.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!doctype struts-config public "-//apache software foundation//
dtd struts configuration 1.1//en"
"http://jakarta.apache.org/struts/dtds/struts-config_1_1.dtd">
<struts-config>
<form-beans>
<form-bean name="approvalform" type="com.i505.struts.approval.form.approvalform">
</form-bean>
</form-beans>
<action-mappings>
<action
attribute="approvalform"
name="approvalform"
input="/index.jsp"
path="/approval"
scope="request"
type="com.i505.struts.approval.action.approvalaction">
<forward name="success" contextrelative="false" path="/resultok.jsp" />
</action>
</action-mappings>
</struts-config>
4.3 registration模块配置文件
下面是registration模块的配置文件,定义了form和action,以及相应的message-resources和forward.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!doctype struts-config public "-//apache software foundation//
dtd struts configuration 1.1//en"
"http://jakarta.apache.org/struts/dtds/struts-config_1_1.dtd">
<struts-config>
<form-beans>
<form-bean name="registrationform" type="com.i505.struts.registration.form.registrationform" />
</form-beans>
<action-mappings>
<action
attribute="registrationform"
input="/index.jsp"
name="registrationform"
path="/registration"
type="com.i505.struts.registration.action.registrationaction">
<forward name="success" path="/resultok.jsp" />
</action>
</action-mappings>
<message-resources parameter="com.i505.struts.applicationresources"/>
</struts-config>
5、模块选择
本节主要讲述struts中如何选择模块,实现模块的真正运作的。
5.1 action的模块选择
当我们在浏览器中使用http://hostaddress/contextpath/module/action.do式样的的url时,actionservlet会根据module选择模块对象,下面是actionservlet处理http请求的代码:
requestutils.selectmodule函数将使用下面的代码把url中的模块前缀(下面代码的prefix将代表上面url式样中的/module)指定的模块对象保存在request属性中,这个模块对象就成了处理这个请求的当前模块对象:
5.2 资源的模块化
资源(比如jsp)的模块化是指资源可以按照模块一样来组织,比如approval模块的资源可以放在approval目录下,而registration模块的资源则放在registration目录下,缺省模块的资源放在webroot下。
url访问这些资源很简单,url式样是 http://hostaddress/contextpath/module/xxx.jsp。对于input和forward访问这些资源,我们只需直接写相对于模块路径下的路径,注意它们必须以”/”开头。如果forward是相对servletcontext的,则要加上模块路径。
5.3 formtag中表单action url的生成
对于模块编程,struts在formtag的action属性好像有些问题,这些问题出现在struts没有考虑直接访问jsp时的情况。应为forward和直接访问这两种环境是不同的,主要是直接访问这些jsp,request属性中没有模块对象,而forward访问这些jsp时request属性中有模块对象。我们需要修改代码,使得在产生action属性时不受jsp所在环境的影响,也就是我们将在formtag的action属性中指定模块,而不是request中得到模块。下面是registration模块的index.jsp的代码,它的formtag的action属性包括了模块的前缀/registration:
下面我们来修改struts的相关代码达到这个效果。
5.3.1 formtag
formtag的setaction将识别form tag的acton属性的module前缀,并分离出真正的模块相对的action路径,lookup将直接从servletcontext中获取模块配置对象。
(this.moduleprefix+ this.action, this.pagecontext))); … }
5.3.2 requestutils
requestutils的getactionmappingurl主要用作附加servletcontext 路径,因为我们现在在action参数附加了moduleprefix路径,所以没必要再追加模块前缀。
6、总结
模块化编程有利于提高编程效率,但是struts中的模块化支持有些小问题,本文详细分析了struts支持模块化编程的机制,并作了些修改,希望对大家有帮助。另外如果我们可以把其改进为模块化的相关的东西可以打成一个包进行动态部署(比如approval.mar)的话,那将会更加有用。

 闽公网安备 35060202000074号
闽公网安备 35060202000074号